GMAT vs CAT: What is the Difference Between GMAT and CAT?
Debating on the battle of GMAT vs CAT, and not sure which one to pick for your MBA entrance exam? Let us help you overcome this dilemma. Both GMAT and CAT exams are the most competitive MBA entrance tests in the world. While both the tests let you take admission to the top MBA colleges, they inherently differ in the syllabus, scope, and exam pattern.
The fundamental distinction lies in the scope of these examinations. The Common Admission Test (CAT) serves as a domestic entrance examination ( while some international universities accept CAT scores), whereas the Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) is an international assessment recognized for admissions to business schools globally. Indian business schools consider GMAT scores typically for NRIs and international students.
Let’s understand the differences between GMAT and CAT which can dispel many of the doubts most aspirants face.

Read More: CAT Syllabus 2025: Sections, Weightage, Exam Pattern, Tips to Prepare
GMAT vs CAT – Overview of GMAT and CAT
The Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) and the Common Admission Test (CAT) are standard exams for business school admissions, but they serve different purposes. GMAT is used globally, especially for MBA programs abroad, while CAT is India-focused, mainly for IIMs and other Indian MBA colleges.
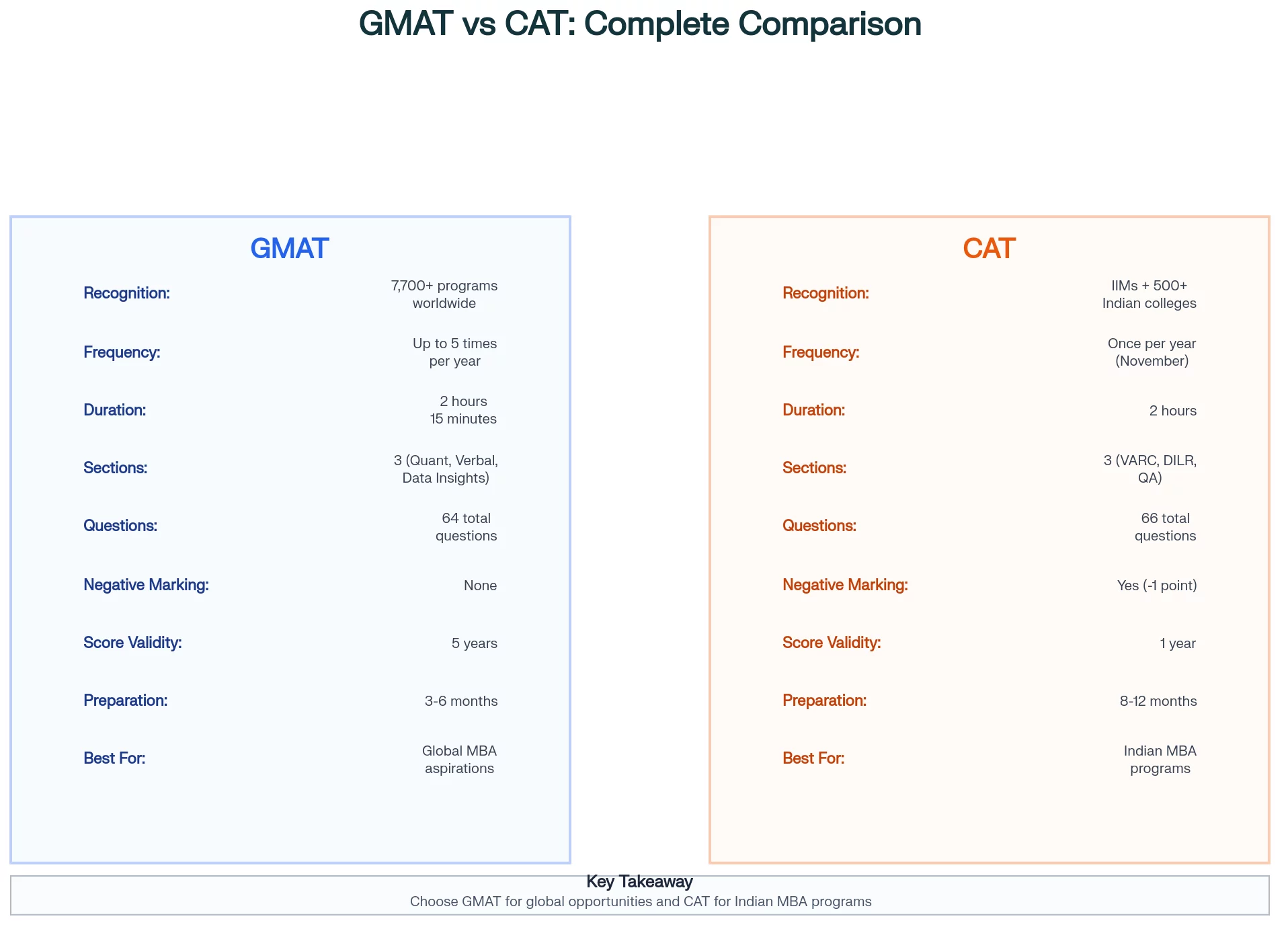
The table outlines the key differences between the GMAT and CAT exams:
| Parameters | GMAT | CAT |
| Conducting Body | Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC) | Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs) |
| Full Form | Graduate Management Admission Test | Common Admission Test |
| Exam Frequency | Available year-round; up to 5 attempts per year | Once a year, typically in November |
| Exam Duration | Approximately 2 hours and 15 minutes | 2 hours |
| Paper Pattern | Computer Adaptive Test
|
Computer Based Test
|
| Number of Sections |
|
|
| Number of Questions |
|
|
| Duration for Each Sections | 45 minutes per section | 40 minutes per section |
| Marking Scheme |
|
For MCQs
For Non MCQs
|
| Total Scores | Total score ranges from 205 to 805 | Maximum score: 198
Scores are presented as percentiles. |
| Score Validity | 5 years | 1 year |
| Negative Marking | No | Yes, -1 for incorrect multiple-choice answers |
| Acceptance | Accepted by over 7,700 programs worldwide, including top global business schools | Primarily accepted by Indian business schools, including all IIMs |
| Difficulty Level |
|
|
GMAT Vs CAT: Scope and Competition
GMAT
Over 2000 business schools accept scores of GMAT Focus Edition for MBA and Master’s programs. In India, prestigious B-schools like ISB and IIMs accept GMAT scores as well. GMAT is ideal for students who aim for international or top-tier Indian programs. Annually, ~200,000 aspirants appear for GMAT exam.
CAT
The IIMs and non IIMs in India accept the CAT score for their admission program to the PGDM/MBA. On average, almost 3 lakhs aspirants register for the CAT exam that directly increases its competition compared to GMAT.
Both the exams evaluate the candidates on the basis of quantitative skills. However, there is a distinction in one of the sections. The GMAT tests verbal reasoning and data insights, whereas the CAT focuses on verbal ability and reading comprehension in addition to data interpretation and logical reasoning.
GMAT scores are valid for 5 years, compared to 1 year for CAT scores, and the GMAT allows up to 5 attempts per year. While the GMAT offers immediate unofficial scores and results within 3-5 business days, CAT results are released after a month. Notably, the GMAT doesn’t have negative markings, unlike the CAT. The GMAT is accepted globally, while the CAT is primarily for Indian business schools.
GMAT vs CAT Difficulty: Which Is Harder and Why?
Whether the GMAT or the CAT, both are highly respected and test similar skills. However, they differ in overall difficulty level. Understanding these differences is essential before deciding where to focus your preparation.
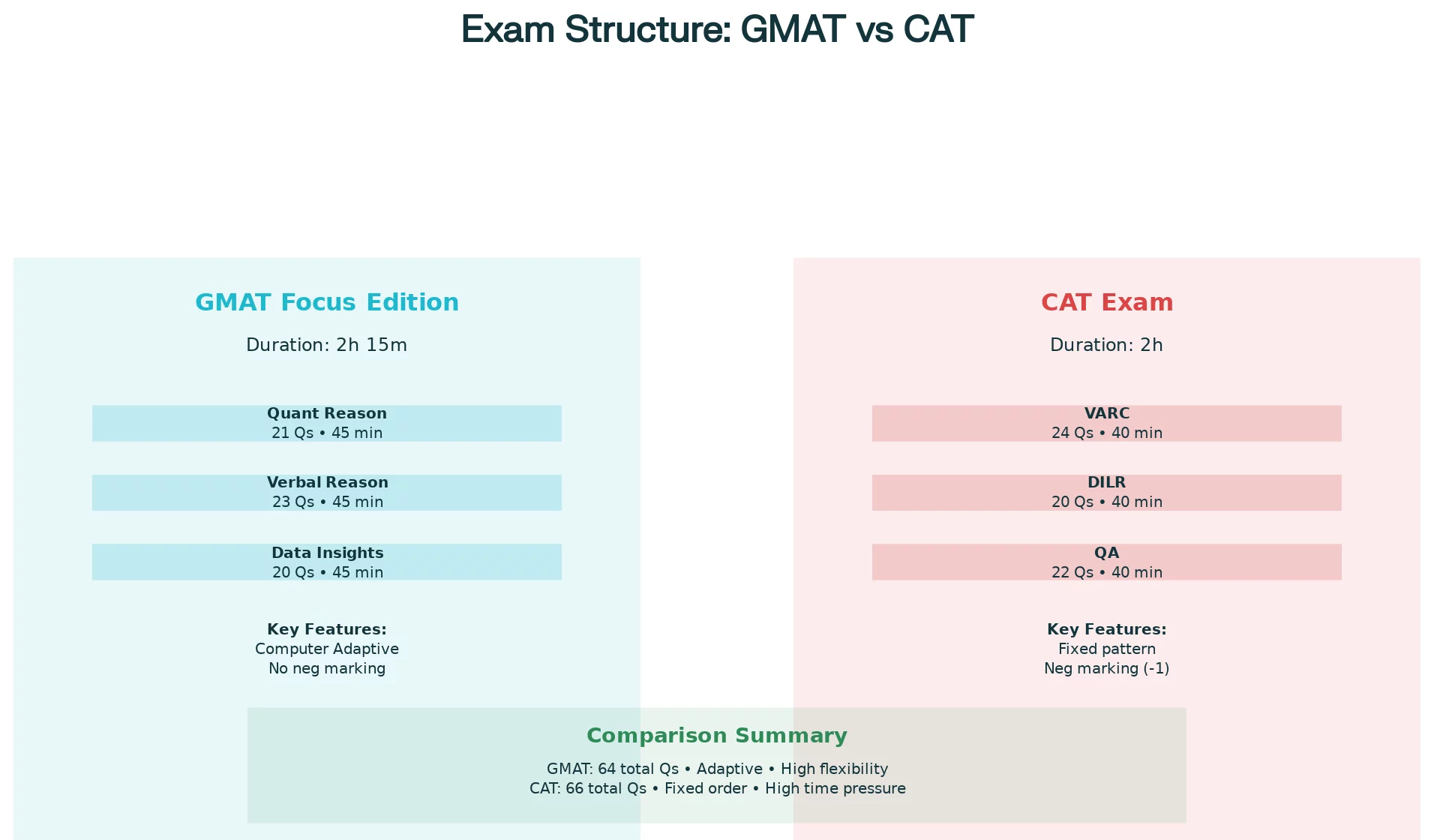
- Duration: The GMAT exam’s duration is 2 hours and 15 minutes with an optional 10-minute break, while the CAT runs for 2 hours with no breaks.
- Sections: The sections under GMAT are, Quantitative Reasoning, Verbal Reasoning, and Data Insights, whereas the CAT includes Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC), Data Interpretation & Logical Reasoning (DILR), and Quantitative Ability (QA).
- Questions: The total questions are almost similar. The GMAT has 64 and CAT has 66 questions. But the paper structure makes a big difference. The GMAT gives you 45 minutes per section, while the CAT allots 40 minutes per section, which can make pacing more difficult.
- Negative Marking: Another major distinction is negative marking: GMAT has none, but CAT penalizes incorrect answers with 1 negative mark for each incorrect answer.
- Flexibility: One of the biggest advantages of the GMAT is flexibility to choose the order of the sections and take a short break in between. The CAT exam has a fixed order to attempt the sections without any breaks.
- Test Pattern: Moreover, the GMAT is computer-adaptive, meaning the difficulty of each question adjusts based on your previous responses, while the CAT follows a fixed pattern.
- Scoring Pattern: In terms of scoring, the GMAT uses a scaled score between 205 and 805, along with a percentile. The CAT provides only percentile rankings based on relative performance.
Conclusion:
When comparing the two, the CAT feels more rigid and time-pressured, while the GMAT offers a more structured and flexible testing experience. The absence of negative marking and the adaptive nature of the GMAT make it less intimidating for many students. However, CAT’s unpredictable pattern and tougher time limits test your composure and speed under pressure.
CAT Vs GMAT – Exam Content and Structure
GMAT (Graduate Management Admission Test)
The GMAT Focus Edition comprises three sections:
- Quantitative Reasoning: Assesses problem-solving abilities and understanding of basic mathematical concepts.
- Verbal Reasoning: Evaluates reading comprehension, critical reasoning, and sentence correction skills.
- Data Insights: Measures the ability to evaluate information presented in multiple formats, including data sufficiency, table analysis, graphics interpretation, multi-source reasoning, and two-part analysis.
Each section consists of a specific number of questions and is timed at 45 minutes, totaling 2 hours and 15 minutes for the entire exam. The GMAT is a computer-adaptive test, meaning the difficulty of questions adjusts based on the test-taker’s performance.
CAT (Common Admission Test)
The CAT exam comprises three sections:
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC): Tests English language skills and comprehension.
- Data Interpretation & Logical Reasoning (DILR): Assesses the ability to interpret data and solve logical problems.
- Quantitative Aptitude (QA): Evaluates mathematical skills and problem-solving capabilities.
Each section is allocated 40 minutes, making the total exam duration 2 hours. citeturn0search3
Unlike the GMAT, the CAT is not adaptive; all candidates receive the same set of questions.
Read More: CAT Preparation
GMAT Preparation 2025 Tips: Strategy, Section-Wise Tips
CAT Vs GMAT Syllabus
Both the GMAT and CAT assess analytical, quantitative, and verbal reasoning skills with a different approach.
- Complexity: The GMAT has a clearly defined and structured syllabus, making preparation more predictable. The CAT syllabus, however, is less formalized and can vary from year to year, which often adds to its complexity.
- Quantitative Section: The Quantitative section of the GMAT focuses on logical problem-solving rather than advanced mathematics, making it slightly less challenging than CAT’s quant section. CAT’s Quantitative Ability section covers a broader range of topics, including geometry, algebra, and arithmetic, and often features more complex problem types.
- Verbal Section: The GMAT tends to be more difficult, with questions on strong grammar, logic, and comprehension skills. CAT’s Verbal Ability and Reading Comprehension (VARC) section is slightly easier, but can feel tricky due to ambiguous answer choices and lengthy reading passages.
- DILR Section: In Data Interpretation and Logical Reasoning, CAT is notably more demanding. The questions often include puzzles, seating arrangements, and intricate data sets that require deep analytical thinking. GMAT’s Data Insights section is comparatively direct, focusing on the interpretation of charts, graphs, and case-style problems.
GMAT vs CAT – Eligibility
When comparing the eligibility criteria for the GMAT and CAT exams in 2025, there are some key differences to note.
GMAT
The GMAT (Graduate Management Admission Test) is globally acceptable with minimal eligibility restrictions. Candidates must be at least 13 years old, though those under 18 require parental consent. There is no upper age limit, and notably, no specific educational qualification is required to take the exam. There are also no minimum academic marks needed, and even those in their final year of studies, or without a formal degree, can attempt the test. However, individual B-schools accepting GMAT scores may set their own admission requirements. Candidates can take the GMAT up to five times in a rolling 12-month period, with a lifetime cap of eight attempts.
CAT
On the other hand, the CAT (Common Admission Test) is largely relevant in India. Primarily, IIMs and other top MBA colleges in India accept CAT scores for their admission cycle. To be eligible for CAT 2025, candidates must have a bachelor’s degree from a recognized institution with a minimum of 50% marks (or 45% for SC/ST/PwD candidates). Final-year undergraduate students are eligible to apply as long as they complete their degree within the required timeframe. There is no age limit for CAT and no restriction on the number of attempts, making it more accessible in that regard. However, unlike GMAT, CAT has stricter academic prerequisites and is intended largely for Indian nationals (though some IIMs accept GMAT scores from foreign nationals for international admissions).
GMAT vs CAT- Preparation and Strategy
GMAT
Preparation typically takes between three to six months. The GMAT allows flexibility in scheduling, as it can be taken multiple times a year, enabling candidates to choose a date that aligns with their readiness.
CAT
Candidates need to dedicate around a year to prepare for the CAT due to its unpredictable nature and the intense competition. Strategic planning is crucial since the CAT is conducted only once a year.
What to choose when deciding between the GMAT and CAT depends on individual career goals, target institutions, and personal strengths. The GMAT offers global opportunities with flexible scheduling, making it suitable for candidates aiming for international business schools or specific programs within India. Conversely, the Common Admission Test (CAT) is imperative for individuals aspiring to enroll in prestigious Indian institutions such as the Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs). A comprehensive understanding of the distinguishing characteristics of each examination will enable candidates to make judicious selections that are congruent with their professional objectives.
Read More: MBA vs MIM: Which One Should I Pursue?
Top 20 MBA Schools in the US
FAQs
CAT vs GMAT, which one is more rigorous?
The CAT exam is more rigorous as its syllabus is undefined compared to that of the GMAT exam. Additionally, the CAT exam has broader quantitative section and required longer preparation time almost for 8–12 months for a good percentile score.
On the other hand, GMAT has a structured syllabus and it requires only 2–3 months of focused preparations.